All living organisms need food to survive. Food is obtained from plants and animals.
The branch of science that deals with growing plants and raising livestock for human use is called Agriculture.
Cultivation of crops and rearing of animals have undergone tremendous advancement during the last century. The increasing human population has been a contributing factor. In order to provide food for the increasing population, regular production, proper management, and distribution of food are necessary.
CROP PLANTS
When a large number of plants are grown at the same place for food, it is called a crop. A large number of wheat plants grown in a field make up a crop of wheat.
The branch of agriculture which deals with ornamental and fruit plants is called horticulture.
Classification of Crops
Crops have been classified as cereals, pulses, vegetables, fruits, oilseeds, fibre producing plants, medicinal plants, etc. According to the seasons, crops can be classified as follows :
Kharif crops are sown during June- July (at the beginning of the monsoon season) and harvested at the end of the monsoon during September and October. Paddy or rice requires a lot of water and is a Kharif crop. Maize, soya bean, and cotton are other examples of Kharif crops.



Rabi crops are sown during October December (at the beginning of winters) and harvested in March and April. Wheat, gram and mustard are some examples of rabi crops.



AGRICULTURAL PRACTICES
Farmers do very hard work to get maximum production from the fields, for this they use different methods of skills which are called agricultural practices. Agricultural practices are specific methods that, when applied to agriculture, create food for consumers or further processing that is safe and wholesome. There are certain conditions that are very important for ensuring a high crop yield. In order to grow well and healthy plants or crops, the right type of soil, ploughing, seeds, proper handling of animals, proper irrigation methods, and use of manures and fertilizers are needed. This includes proper pest control, use of harvesters and threshers. When agricultural practices are carried successfully by using old or modern tools, these are known as farming implements.
Preparation of Soil
Soil anchors the roots of plants provide nutrients and water to them, and also provides oxygen to the roots. The microbes and other organisms, such as earthworms in the soil, help to keep it fertile. Therefore, it is very important that the soil must be well prepared.
Preparation of soil requires two steps Ploughing and Levelling.
The first step in the preparation of soil required is loosening and turning of the soil.
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called ploughing or tilling.
This has the following advantages :
- Ploughing makes the soil loose and porous.
- The roots of seedlings can penetrate the loosened soil easily.
- When the roots grow deeper and spread out the plant is anchored well to the soil.
- Water drains easily in loosened soil. This helps roots to breathe and not drown.
- Ploughing helps to aerate the soil. This helps microorganisms and earthworms present in the soil to make the soil fertile.
- Fertilizers and manure can be mixed well with the loosened soil.
- Ploughing uproots weeds, which on decomposition make the soil fertile.
The instrument used for ploughing is called a plough. Plough may be made of wood and iron or of iron only. For ploughing of the soil, domestic animals like ox and camel are used.

Plough
Now, in big farms, the tractors are used for ploughing with a cultivator which saves time and labour of ploughing manually. The process of making the soil surface even and smooth is called levelling. The process is done with the help of a wooden soil leveller.
Levelling ensures uniform irrigation and distribution of minerals in the field. It helps to prevent soil erosion.
Selection and Sowing of Seeds
Before sowing, the selection of seeds of good quality is very important so that the yield is good. Seeds are sown by the traditional method of using a funnel-like instrument where the seeds are put into the funnel and placed into the soil through attached tubes. Sowing can also be done manually by scattering seeds and spreading them into the field. This is called broadcasting.
A seed drill has a funnel-shaped opening leading to long tubes. It is attached to a plough. Seeds are put into the funnel. As the plough makes furrows in the soil, the seeds are deposited in the soil by the drill.
The seed drill sows the seeds at equal distances and proper depth. This ensures that the seeds also get covered by soil after sowing. This saves them from being eaten by birds.
Transplantation
Transplantation of paddy image
It is the process of transferring healthy seedlings from the plot (nursery) to the main field. Transplantation is common in the cultivation of paddy and vegetables.
During transplantation, seedlings are planted in a well-prepared field at a proper distance in rows. This ensures that plants are able to receive sufficient light, water, and space.
IMPROVING SOIL FERTILITY
Crop plants require nutrients for growth. These are obtained from the soil. When a farmer grows crops continuously in the same field, the soil becomes poor in nutrients. As a result, the crop yield gets reduced.
There are three ways to overcome this problem:
Natural methods
Field fallow: One way of allowing land to naturally regain the nutrients is to leave it free for fallow) for one or more season Dead plants animals and other organic matter that collect on the land are decomposed by microbes Thus, the nutrients are returned to the soil
Crop rotation: When a crop is grown season after season for many years, the set of nutrients that the crop needs is used up When the same crop is grown again the yield will be poor To prevent this from happening the crops grown in a field should be changed every year Growing different crops in a field over successive years to avoid depleting the nutrients in the soil is called crop rotation
Multiple cropping: Growing two or more crops together in the same field at the same time is called multiple cropping. For example, a cereal like wheat can be grown with a legume like a pea. The wheat plant uses the nitrates in the soil and the Rhizobium bacteria in the root nodules of the pea replace the nitrates by converting atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates.
However, these natural methods alone are not enough to maintain the fertility of the soil, so farmers have to add manures and fertilisers from time to time.
ADDING MANURE TO THE FIELD
The fertility of agricultural lands can be enriched by adding manure. Manure is mainly decomposed animal dung and plant material. It contains a large amount of fibre. The fibrous nature of manure increases the water-holding capacity of the soil and also makes it more porous. Porous soil is good for the plants because it holds more air and keeps the roots healthy. Another good method of maintaining soil fertility is growing crops like beans and gram, which have the natural ability of making soil fertile.
Cow manure is abundantly available and is an environment friendly fertilizer and soil amendment as opposed to chemical products In adds valuable nutrients to the soil thereby allowing flowers and vegetables to thrive.
Applying chemical fertilisers
Plants need minerals such as potassium (K) and phosphorous (P), and salts like nitrates to grow. Often, manures are not adequate to replenish these plant nutrients in the soil. Therefore, farmers use chemical fertilisers that mainly contain nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
Excessive use of chemical fertilisers damages the soil. They make the soil les porous and reduce the water holding capacity of the soil. Chemical fertilisers also make the soil acidic. Most plants do not grow in acidic soil.
Irrigation
Irrigation means supplying water to the crops in the fields at specific intervals.
Water is important for crops as:
Germination of seeds does not take place without water.
Roots fail to develop and elongate in dry soil.
Nutrients cannot move up from the soil in the absence of water.
It protects the plant from frost and hot air currents.
Thus, water is essential for the proper growth and development of crop plants. Water is absorbed by plants from the soil through the root system. Along with water, minerals are also absorbed.
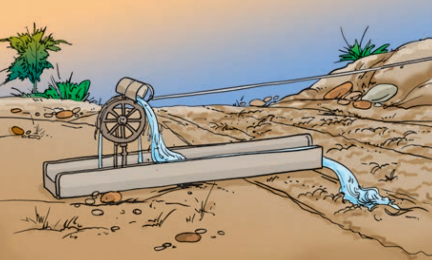
Traditional Methods of Irrigation
In these methods, cattle or human labour is used. Hence these methods are cheaper but less efficient. The different traditional methods are moat, chain pump, rahot, dhekli, etc.



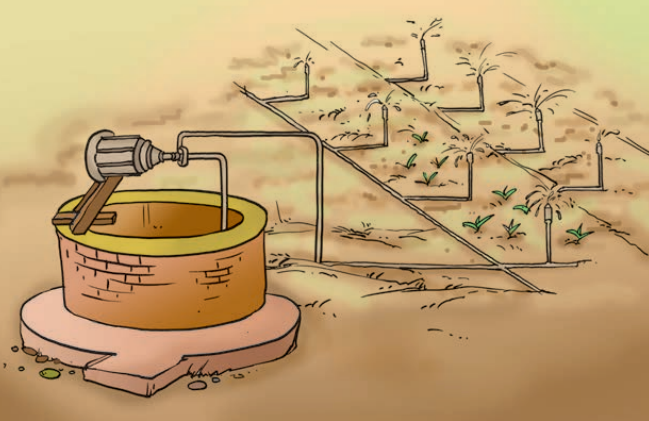
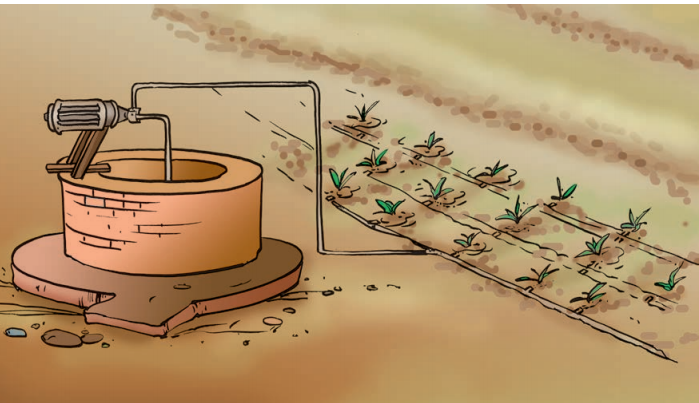
Some of the modern irrigation methods are as follows:
- Sprinkler system: This is a method by which water is sprinkled over the field by rotating sprinklers. The water flows to the main pipe and then to the small pipes with the help of a pump. This method is good for uneven lands, lands with less availability of water and sandy regions.
- Drip irrigation: It is a method by which water is allowed to fall only on the roots drop by drop. The method is excellent for regions with low water availability as in the method there is no wastage of water.
Weeding
Weeds are unwanted and uncultivated plants that grow along with the crop plants. If you visit a field, you will notice many weeds growing with the crop plants. These weeds are not grown by the farmer. They grow on their own. Some examples of common weeds are:
Amaranthus (chaulai), Chenopodium (bathua) and wild oat (javi).
The process of removing weeds from a field is called weeding. Weeding can be done manually by pulling the weeds out by hand or by using a trowel or a harrow to uproot them.
Weeding is also done by spraying special chemicals called herbicides or weedicides, with the help of a sprayer. They destroy the weeds but do not affect the main crop. Some common weedicides are dalapon, metachlor and siniazine.
Crops are eaten or damaged by large animals (such as cows, goats and birds), small animals (such as mice and rats) and insects (such as locusts, weevils and termites). This can result in the destruction of crops under cultivation. Birds are kept away from fields using scarecrows, light-reflecting strips and so on. Rodents are killed using rodenticides, whereas insects are killed by spraying insecticides on crops.
These different chemicals (weedicides, rodenticides and insecticides) are together called pesticides as they kill specific kinds of pests.
Pesticides are harmful chemicals. They contaminate soil, water and air and affect our health. Hence, pesticides should be used sparingly. Certain plant products are effective in controlling some insect pests. Such products are not harmful and can be used to reduce the use of pesticides.
Certain insects like the ladybird feed on pest insects and can be used to control pests.
Harvesting, threshing and winnowing
Once the crop matures, it is harvested, i.e., cut and gathered. This may be done manually by using a sickle, or by using a machine called a harvester.
Next, the grain is separated from the cut crop. This process is called threshing. Threshing can be done manually or using the machine- thresher or combine.
The process of separating the grains from the chaff with the help of wind is called winnowing .
Storage of agricultural produce
It is not possible to sell the entire harvested produce at one time. The produce has to be stored in a clean place under proper conditions. Different agricultural produce need different kinds of storage facilities.
Vegetables and fruits are preserved in cold storages or by refrigeration process. Cold storages are big rooms or halls in which minimum temperature (freezing temperature) is maintained. Food products are kept safe and fresh in cold storages and supply is done out of seasons also.
Large amounts of grains are stored in godowns called granaries and in grain silos. The granaries are fumigated (treated with chemical vapours) to get rid of pests. These places are also regularly inspected to protect the grains and ensure safe storage.
FOOD FROM ANIMALS
A number of food items like milk, eggs, meat, honey and fish are obtained from animals. Rearing of animals on a large scale with proper food, shelter and care is called animal husbandry. Animals are raised in farms.
Milk is mainly obtained from cows and buffaloes. Goat, sheep, yak and camel milk is also used as food.
Animals that provide us milk are known as milch animals. These animals must be kept in clean sheds with proper ventilation.
Poultry farming
The rearing of birds like chickens, ducks, quails, turkey and guinea fowl for eggs and meat is known as poultry farming.
Fish and other sea foods
A large population of our country depends on fish and other sea foods like prawns and shrimps. Rearing of fish artificially in tanks and ponds is known as pisciculture.
Apiculture
Rearing of bees artificially is called apiculture.
Honey produced by bees is a valuable source of food (carbohydrate) It is also used for making certain medicines.

