Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings (All Activities)
Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings (All Activities)
Here I covered all important point or everything about Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings (All Activities)
Click Here : NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings.
Table of content
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.1 )
- Take a 100 mL beaker.
- Fill half the beaker with water and mark the level of water.
- Dissolve some salt/ sugar with the help of a glass rod.
- Observe any change in water level.
- What do you think has happened to the salt?
- Where does it disappear?
- Does the level of water change?
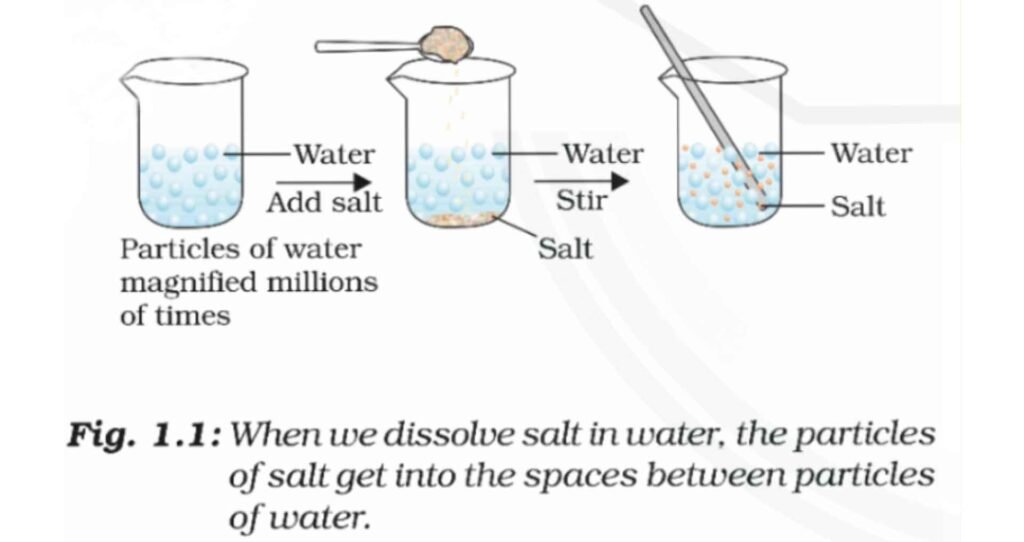
Explanation :
What do you think has happened to
the salt?
- Salt dissolved completely.
Where does it disappear?
- It diffuse in water.
Does the level of water change?
- The level of water does not change when salt is dissolved in water because the salt particles dissociate and occupy the intermolecular spaces between the water particles.
- Since only the empty spaces are occupied, the level of water does not increase.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.2 )
- Take 2-3 crystals of potassium permanganate and dissolve them in 100 mL of water.
- Take out approximately 10 mL of this solution and put it into 90 mL of clear water.
• Take out 10 mL of this solution and put it into another 90 mL of clear water.
• Keep diluting the solution like this 5 to 8 times.
• Is the water still coloured ?
- Take out approximately 10 mL of this solution and put it into 90 mL of clear water.

Explanation :
In activity 1.2 , potassium permanganate dissolve with water and after keep diluting the solution became lighter in colour. Even after 8 time of diluting, colour still visible this show how small particle is.
So, this activity show how small are these particles of matter?
Is the water still coloured ?
- Yes, Water still coloured but every dilution, colour become light, it is still visible.
CONCLUSION
- This experiment conclude that there must be millions of tiny particles in just one crystal of potassium permanganate, which keep on dividing themselves into smaller and smaller particles.
- The same activity can be done using 2 ml of Dettol instead of potassium permanganate. The small can be detected even on repeated dilution.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.3 )
- Put an unlit incense stick in a corner of your class. How close do you have to go near it so as to get its smell?
• Now light the incense stick. What happens? Do you get the smell sitting at a distance?
• Record your observations.

Explanation :
Here, Diffusion occur.
What is diffusion ?
The intermixing of particles of two different types of matter on their own is called diffusion. ( ये तो हो गयी book Ki definition ).
Diffusion is a natural phenomenon and never stops. In our daily life, Diffusion in many places. We add sugar in water to make tea or juices; here sugar molecule diffuses into the water through diffusion. A plant produces oxygen; this oxygen diffuse into the air and we get oxygen for breathing.
What happens? Do you get the smell sitting at a distance?
- Smell of incense stick spread in whole class. Yes, we get the smell sitting at a distance.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.4 )
- Take two glasses/beakers filled with water.
- Put a drop of blue or red ink slowly and carefully along the sides of the first beaker and honey in the same way in the second beaker.
- Leave them undisturbed in your house or in a corner of the class.
- Record your observations.
- What do you observe immediately after adding the ink drop?
- What do you observe immediately after adding a drop of honey?
- How many hours or days does it take for the colour of ink to spread evenly throughout the water?
Explanation :
What do you observe immediately after adding the ink drop?
- Ink particle gradually move into the entire quantity of water and then get mixed the water. (Diffusion take place).
What do you observe immediately after adding a drop of honey?
- After Adding a drop of honey we observe that it does not mixes and goes at the bottom of water.
How many hours or days does it take for the colour of ink to spread evenly throughout the water?
- It take about an hour to spread colour of ink throughout the water.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.5 )
- Drop a crystal of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate into a glass of hot water and another containing cold water. Do not stir the solution. Allow the crystals to settle at the bottom.
- What do you observe just above the solid crystal in the glass?
- What happens as time passes?
- What does this suggest about the particles of solid and liquid?
- Does the rate of mixing change with temperature? Why and how?
Explanation :
What do you observe just above the solid crystal in the glass?
- Solid crystals starts mixing in the water in the form of thread like structures.
- In cold water, thread like structure come slower than of in the hot water.
What happens as time passes?
- As time passes, crystal getting dissolved in water both hot and cold.
- But it take more time to get crystal dissolved in the cold water than that of hot water.
What does this suggest about the particles of solid and liquid?
- This suggest that, matter are made-up of tiny particles and these particles are in the motion continuously.
Does the rate of mixing change with temperature? Why and how?
- Rate of mixing increases with increase in temperature. This is because of heat particles of matter gets more kinetic energy and they starts moving faster.
This happen because :
- Ink has about equal or slightly higher density than that of water. So, ink started immediately mixing with water, because particles of matters are moving continuously.
- Density of honey is very high than that of water, so honey started to direct towards bottom.
Question : On heating, diffusion become faster. Why does this happen ?
Answer : On heating, diffusion become faster because the kinetic energy increasing and the particles start moving with high speed. Particles of matter get in or between the particles of each other speedly.
( So, the conclusion is on heating the rate of diffusion become faster ).
CONCLUSION
- Particles of matter are continuously moving i.e. they possses kinetic energy.
- As the temperature rises, particles move faster.
- On increasing temperature the kinetic energy of particles alos increases.
- The intermixing of particles of two different types of matter on their own is called diffusion.
- On heating, diffusion become faster.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.6 )
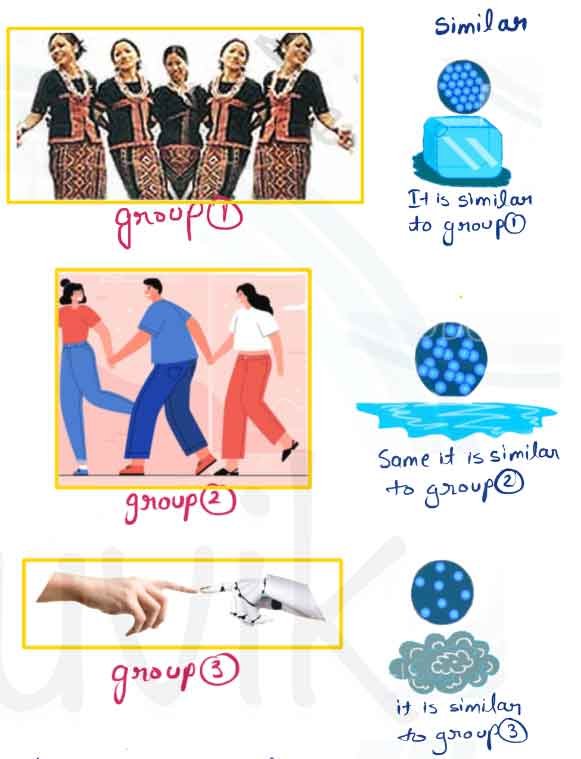
- Play this game in the field— make four groups and form human chains as suggested:
- The first group should hold each other from the back and lock arms like Idu-Mishmi dancers.
- The second group should hold hands to form a human chain.
- The third group should form a chain by touching each other with only their finger tips.
- Now, the fourth group of students should run around and try to break the three human chains one by one into as many small groups as possible.
- Which group was the easiest to break? Why?
Explanation :
- If we observe, group (1) is hardest to break.
- If you saw molecule of group (1) (2) and (3), there molecules are joined to other molecules by force of attraction. This force of attraction keeps them together.
Which group was the easiest to break? Why?
- The group (3) easiest to break, because force of attraction between finger to finger is very less compare to group (1) and group (2).
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.7 )
- Take an iron nail, a piece of chalk and a rubber band.
- Try breaking them by hammering, cutting or stretching.
- In which of the above three substances do you think the particles are held together with greater force?



Explanation :
In which of the above three substances do you think the particles are held together with greater force?
- Hammering a piece of iron nail does not break the nail but flatten its surface.
- Hammering chalk breaks the chalks give us powered chalk.
- We can stretch the rubber band to a large extend without any break.
- All explanation above, clearly we say iron nail particles are held together with the greater force.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.8 )
- Take some water in a container, try cutting the surface of water with your fingers.
- Were you able to cut the surface of water?
- What could be the reason behind the surface of water remaining together?

Explanation :
- We can easily cut the water using finger. Water join again once we remove finger.
- ( Water has a weak attraction force than solids, So, we can easily swirl our finger across it )
- Once we move the finger, water occupies the same space again.
- A similar process also occurs with air, here air molecules regain the empty spaces similarly.
CONCLUSION
- From the above three activities ( 1.6, 1.7, and 1.8 ) show that particles of matter have force acting between them.
- This force keeps the particles together.
- The strength of this force of attraction varies from one kind of matter to another.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.9 )
- Collect the following articles— a pen, a book, a needle and a piece of wooden stick.
- Sketch the shape of the above articles in your notebook by moving a pencil around them.
- Do all these have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and a fixed volume?
- What happens if they are hammered, pulled or dropped?
- Are these capable of diffusing into each other?
- Try compressing them by applying force. Are you able to compress them?
Explanation :
Do all these have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and a fixed volume?
- Yes, they have fixed shape and volume.
What happens if they are hammered, pulled or dropped?
- If they hammered or pulled, they are capable of breaking.
Are these capable of diffusing into each other?
- No, Solid are not capable of diffusing each other but they are capable of diffuse with liquid. ( eg. Tablets dissolve in water )
Try compressing them by applying force. Are you able to compress them?
- No, It is not possible to compress them because solid don’t have space between particles but in case of sponge i.e. compress easily (They are some Exceptions ).
- All Example above are solids.
- All these have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and fixed volumes, i.e. have negligible compressibility.
- Solids have tendency to maintain their shape when subjected to outside force.
- Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, So they are rigid.
Class 9 Matter In Our Surrounding ( ACTIVITY 1.10 )
- Collect the following:
(a) water, cooking oil, milk, juice, a cold drink.
(b) containers of different shapes. Put a 50 mL mark on these containers using a measuring cylinder from the laboratory.
- What will happen if these liquids are spilt on the floor?
- Measure 50 mL of any one liquid and transfer it into different containers one by one. Does the volume remain the same?
- Does the shape of the liquid remain the same ?
- When you pour the liquid from one container into another, does it flow easily?
Explanation :
What will happen if these liquids are spilt on the floor?
- When liquid spilt on the flour. It completely lost their shape.
Measure 50 mL of any one liquid and transfer it into different containers one by one. Does the volume remain the same?
- Yes, Volume remain the same .
Does the shape of the liquid remain the same ?
- However, the shape of liquid changes as per container design. So, the shape of the liquid not remain same.
When you pour the liquid from on container into another, does it flow easily?
- Yes, it flows easily while transferring to another container.
Liquid have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume.
Liquid flow and change shape, so they are not rigid but can be called fluid.
If you want of this chapter then click here Chapter 1 Notes


