MICROORGANISMS
The Earth is home to a tremendous variety of living things, many of which cannot be seen with the naked eyes. The existence of these tiny organisms was not known for a long time. It was only with the invention of the microscope that the present number and variety of these organisms were understood.

Long ago, in 1677. Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch scientist was looking at a drop of pond water under a crude microscope, he had made He found tiny living things moving about in the water. He called them tiny organisms or microorganisms (micro means very small). Microorganisms are also known as microbes.
These organisms have a great impact on humans in many ways Some can cause illness, whereas others can cure diseases. Some supply us with food, whereas others spoil food.
The study of microorganisms is known as microbiology. Scientists who study microorganisms are known as microbiologists.
Where Do Microorganisms Live?
Microorganisms are found everywhere in nature:
- In air water and soil
- On the surface of objects and living organisms
- Inside the bodies of animals including humans and
- In a dead and decaying organic matter
They can survive in all types of environments ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs and dry deserts to marshy places.
TYPES OF MICROORGANISMS
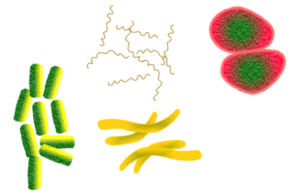
Microbes are of many types and in fact, outnumber plants and animals. They can be classified widely into bacteria, protozoa, fungi, algae, and viruses.
Bacteria are rod-like, spherical, or spiral in shape. Some bacteria are heterotrophic. They depend on other living things for food. Some bacteria are autotrophic that is, they make their own food. Autotrophic bacteria contain chlorophyll and make food through the process of photosynthesis. They are called photosynthetic bacteria. The blue-green algae are photosynthetic.
Protozoa
Protozoa are unicellular organisms that have animal-like characteristics. They can move from place to place. They capture and eat food. Some protozoa live in fresh or saltwater. Others live in the soil. Some are parasites that live in the bodies of other organisms, including human beings. Amoeba, Giardia, and Paramecium are some examples of protozoa.


Fungi
Fungi are present everywhere from deserts to very cold regions but they grow best in dark, warm, and moist places. Fungi are of different sizes. Some are unicellular and some are multicellular. Fungi do not have roots, stems, leaves, or flowers and they do not contain chlorophyll so they are either saprophytic or parasitic.
They may be unicellular, like yeast, or multicellular, like mould. Some like mushrooms are large. Fungi reproduce through spores.

Algae
You have seen the water of a pond that looks green. The water looks green because of the algae growing in it. Some of these algae are unicellular.
Algae are extremely widespread. Most live in water while a few grow on land. Unlike bacteria, unicellular algae have a distinct nucleus. They contain chlorophyll and photosynthesis like plants.
Some algae such as the seaweeds are multicellular and form large colonies. Multicellular algae are classified as plants, but they do not have flowers, seeds, true leaves, roots, or stems.

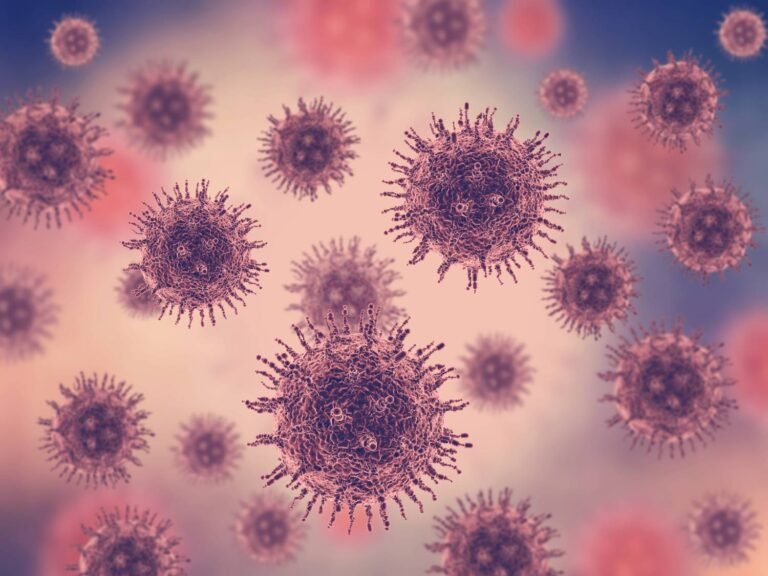
Viruses
Viruses (Virus = meaning poison) are the microscopic and most primitive organisms known to man. They show the characteristics of living as well as non-living beings. They are so small that cannot be seen by a light microscope. They are only visible with an electron microscope. Viruses do not have a cellular structure like other microorganisms. A virus consists of a single strand of nuclear matter (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat. They multiply or replicate only in the host cells. Viruses can be crystallized and stored for many years. Viruses obtain nourishment from their host cells.
USEFUL MICROORGANISMS
Microorganisms are useful in the following ways:
- In the food and beverage industry
- In making medicines and vaccines
- In agriculture
- In cleaning the environment
Making curd and cheese
The process by which a microbe breaks down carbohydrates to form acid or alcohol and carbon dioxide is called fermentation. The bacterium Lactobacillus is added to milk to convert it into curd. Milk contains a kind of sugar called lactose. The bacteria convert lactose into lactic acid and thus make the milk acidic. This acidic environment helps milk proteins to coagulate and form curd.
Yeast is commonly employed in preparing food items like bread, cake, idli dosa dhokla, etc. Have you noticed the tiny air bubbles in cakes, breads and even idlis? This is because the yeast in the dough respires anaerobically and ferments the dough to produce carbon dioxide gas which leaves behind holes as it moves up. The dough hence rises. Yeast is also used in breweries for making wines by the process of fermentation. In this process, the yeast ferments the sugar to form alcohol.

The process of fermentation of sugar by yeast is used in the manufacture of alcohol and alcoholic drinks such as beer and wine. One of the main differences between wine and beer production is the source of the sugars. Wine is prepared by fermentation of sugar in grapes, and beer by fermentation of sugar in germinating barley.
Microbes in the field of medicine
Microorganisms like fungi and bacteria are used to prepare medicines called antibiotics that treat diseases in humans or animals or even plants. The first antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered by Alexander Fleming using the fungus Penicillium. Some other common antibiotics are streptomycin and terramycin.
Making vaccines
When a microbe enters our body the body produces specific substances called antibodies that help to destroy the microbe. A person has immunity against a disease when a certain amount of that specific antibody is present in the body. This immunity can be artificially produced by vaccinating the person. A vaccine is a substance that is given to protect an individual from diseases.
In agriculture to increase soil fertility
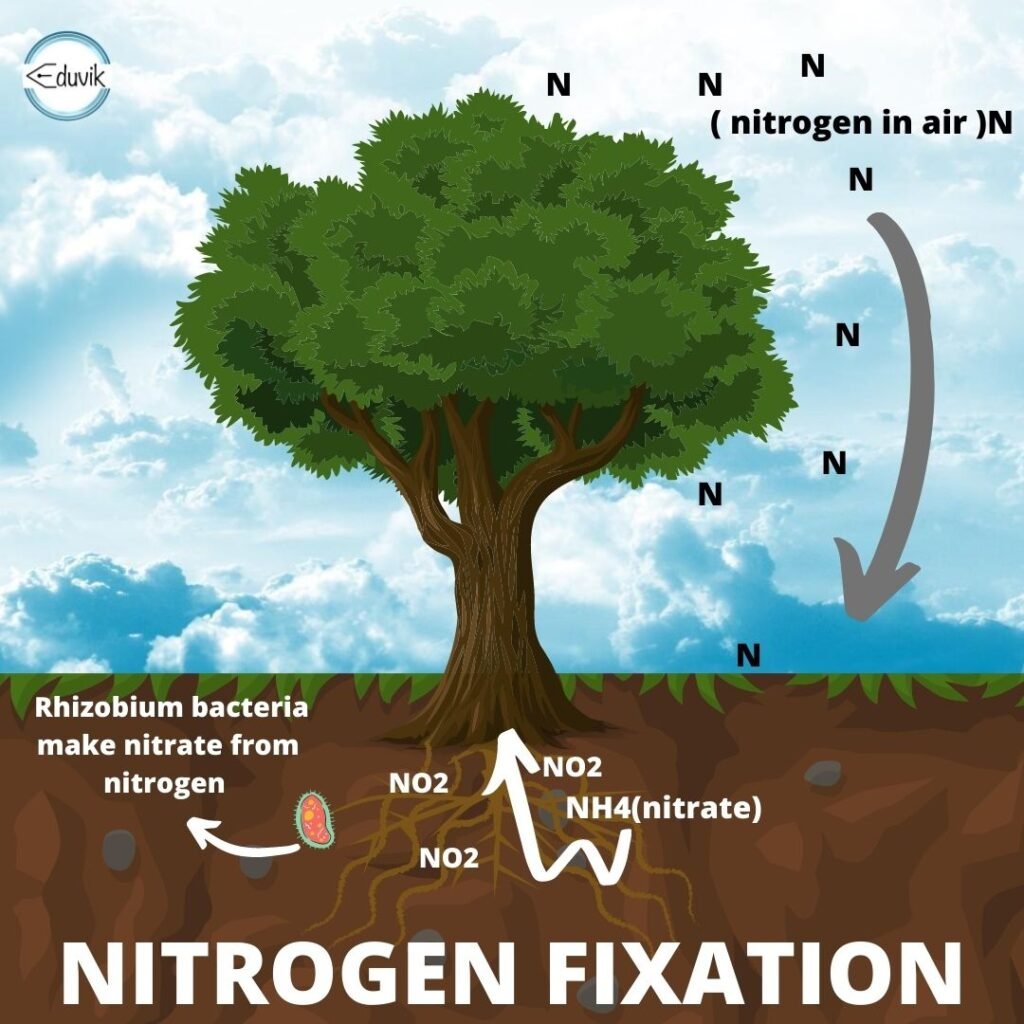
Some bacteria live in the roots of leguminous plants such as pea bean and gram. These bacteria form root nodules and are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into suitable usable forms like nitrates.
Atmospheric nitrogen cannot be used by plants as such, but it can be used in the form of nitrates. The process of fixation of atmospheric nitrogen into suitable forms (that plants can use) is called nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation increases the fertility of the soil.
Blue-green algae are also known to fix nitrogen and increase soil fertility.
In cleaning the environment
Microorganisms such as bacteria fungi and protozoa help by decomposing the tissues of dead organisms to get their food Without bacteria piles of dead organisms would cover the Earth.
When microorganisms decompose organic matter they break down plant and animal tissues into
simple substances, which are restored to the soil. Thus, the nutrients that were taken from the soil by
plants and animals are restored and are used again by living organisms.
Bacteria are used in sewage treatment plants to break down plant and animal matter in sewage. They are also used to make biogas from animal and plant wastes.

HARMFUL MICROORGANISMS
Microorganisms are harmful in many ways. Some of the microorganisms cause diseases in humans, plants, and animals. These disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens and are commonly known as germs. Some microorganisms spoil food, clothing, and even leather. Let us study more about their harmful activities
Diseases causing Microorganisms in Humans
Viruses contain pathogens that are infectious agents that cause diseases. Pathogens enter our bodies through the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the food we eat. They can also get transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or carried through an animal. These kinds of microbial diseases are called communicable diseases. They spread from the infected persons, for example, the common cold, chickenpox, tuberculosis, typhoid, hepatitis, and many more.
Infections through Air
Bacteria, spores of fungi, and viruses enter our body through breathing and attack our windpipe and lungs. Microbes are present in saliva and mucus. When an infected person sneezes or coughs in public places, droplets with the germs are sprayed in the air which is taken by other healthy persons and get infected.
Infection through Water
Water is polluted in so many ways. Sewage is the biggest problem to pollute water. Contaminated water is the cause of jaundice, dysentery, cholera, typhoid, and other intestinal infections. By using unclean water for drinking, brushing teeth, washing the clothes and for cooking purposes, many diseases of the eyes, ears, respiratory system, and intestine may occur. Some infections may take place through swimming pool water. Mosquitoes are carriers for germs causing malaria, dengue, fever, and yellow fever. Malaria is actually caused by a pathogen called Plasmodium which is transmitted by the female Anopheles mosquito. The female Aedes mosquito acts as a carrier for the dengue virus.
Prevention of Communicable Diseases
Some simple methods of limiting the spread of communicable diseases are to keep the infected person separated from others and to advise every person to keep a handkerchief on the nose and mouth while sneezing. How can we protect ourselves from the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue? Among the various methods that can be adopted, the most important measure is to prevent mosquitoes from breeding. We should not allow water to collect anywhere in our neighborhood. We should wash our hands properly before eating. We should never let garbage collect in the neighborhood. This will check the spread of diseases by vectors or carriers like flies and fleas. From time to time vaccinations against diseases should also be taken. In the case of tuberculosis. BCG vaccine is given to the patient.
Microbes Harmful for Plants
- Crown gall disease in cotton is caused by a bacterium.
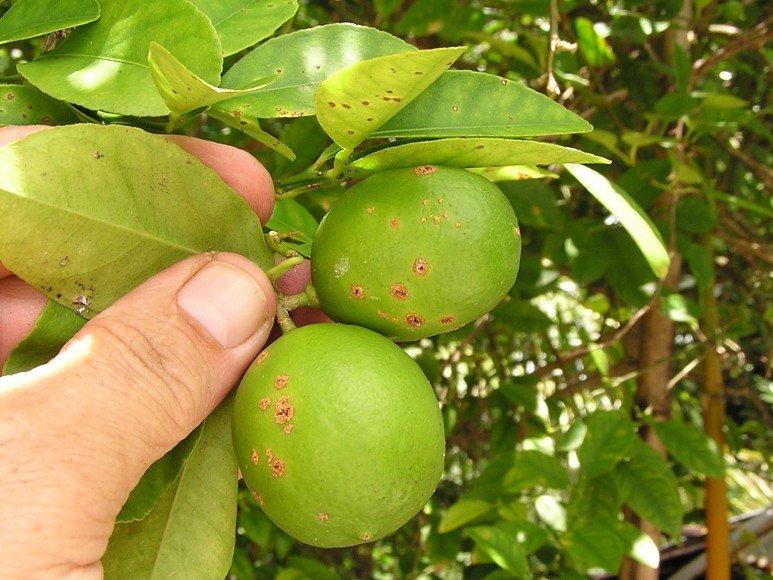
- Citrus canker is a disease caused by a bacterium in citrus plants. Lesions are formed on leaves, stems, and fruits.
- Rice blast is caused by a fungus. It causes lesions to form on all parts of the plant.
- Panama wilt is a fungal disease that affects banana plants.
- Red rot of sugarcane is caused by a fungus.



Diseases causing Microorganisms in Animals
Several microorganisms not only cause diseases in humans and plants but also in other animals. Anthrax is an infectious bacterial disease in sheep and cattle. This disease can be transmitted to humans through the meat, wool, hair, and skin of the affected animals. Foot and mouth disease is a viral disease in sheep, cattle, goats, and horses. Bird flu is also a viral disease in poultry.
FOOD SPOILAGE
Microorganisms spoil food. Many bacteria and fungi grow on food items and produce certain toxic substances. This makes the food unfit for consumption. Many packed juices are often contaminated with yeast which causes fermentation and renders them useless. If such contaminated food is consumed, it can lead to the development of symptoms of food poisoning like nausea, vomiting. abdominal cramps, and diarrhoea.
FOOD PRESERVATION
Food preservation is the name for a number of processes that help to preserve food. A variety of methods are followed to stop food from spoiling
Dehydration: Dehydration is one of the oldest methods of food preservation. It removes moisture from food and so stops microbes from growing on it. Dehydration also decreases the weight of the food, making it easier to store and transport.
Heating: Heating food to a high temperature kills microbes. For example, milk and water are boiled to kill microbes. Ultra-heat treatment (UHT) is the partial sterilization of milk by heating it for a short time, around a couple of seconds, at a temperature exceeding 135 °C. UHT milk available in tetra packs has a shelf life of 6 months or more until opened.
Refrigeration and freezing: Like boiling, cooling by refrigeration and freezing also helps to preserve food items. Refrigeration and freezing do not kill microorganisms, but only stop them from growing and multiplying.
Preservation by freezing is effective for many months and is useful in the case of milk, meat, and vegetables.

Pasteurisation: This method is used for preserving milk.
In this method,
(i) milk is heated to about 70°C for about 15-30 seconds, and
(ii) then quickly cooled (chilled) and stored in sterilised bottles or pouches.
Heating kills the bacteria present in milk. Quick cooling prevents remaining bacteria from growing. Milk products like cheese and other substances like honey, beer, wine, juices, etc. are also preserved using this method.
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist. He discovered the method of pasteurisation and microbial fermentation.
Adding preservatives: Some edible substances either kill microbes or prevent their growth Oil and vinegar are examples of substances that prevent microbial growth. Food materials are pickled in oil and vinegar to store for a long time. Vegetables, fruits, fish, and meat can be preserved this way.
Salt, check the growth of bacteria by forcing microorganisms to lose water by a process called osmosis. It is used for preserving meat, fish, pickles, chips, etc.
Sugar inhibits the growth of bacteria and is used as a preservative in jams, jellies and squashes. It also makes microbes lose water by osmosis.
Canning: Food items are enclosed in cans which are sealed and heated to 120°C to destroy microorganisms, Canned food can remain good to eat for years, provided the cans are not damaged. Dry fruits and vegetables are preserved by this method.

